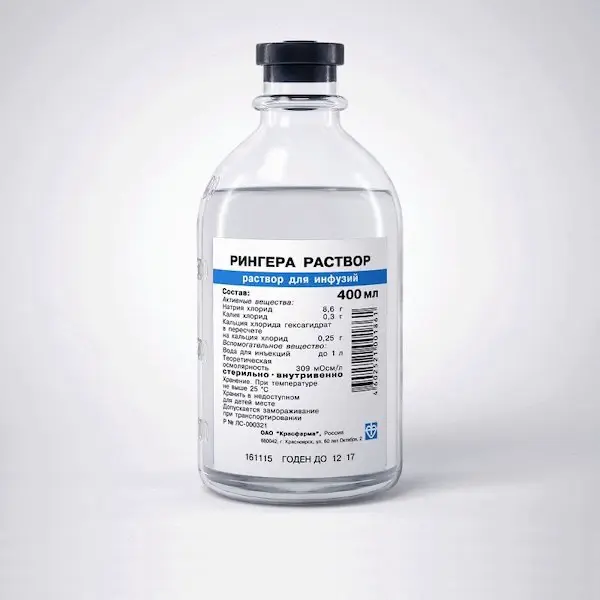
Description
Ringer Solution Pharmacodynamics
Rehydrating agent, has a detoxifying effect, restores water and electrolyte composition of blood. When used as a remedy for replenishment of circulating blood volume (RBC), due to quick} exit from the bloodstream into the exgravasal space, the effect lasts for only 30-40 minutes (therefore, the solution is suitable only for short-term replenishment of the RBC).
The main cation of extracellular fluid sodium is involved in the control of water distribution, water balance, osmotic pressure. It also binds with chlorine and bicarbonate in the regulation of the body’s acid-base balance.
The main cation of intracellular fluid, potassium is involved in protein synthesis, carbohydrate synthesis, nerve impulse conduction and muscle contraction. Calcium in ionized form is necessary for the functional mechanism of blood clotting, normal heart function, and regulation of neuromuscular excitability. The main extracellular anion chlorine is closely related to sodium metabolism and participates in regulation of acid-base balance of the body.
Indications
Dehydration and electrolyte balance disorder (3rd and 4th degree thermal burns, frostbite, prolonged vomiting and diarrhea), acute blood loss, correction of water-salt balance in acute septic peritonitis and intestinal obstruction, acute intestinal infections (severe course, inability to take oral dehydrating agents), hypovolemic shock, therapeutic plasmapheresis.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to drug components, hypernatriemia, hyperchloremia, hypercalcemia, hyperkalemia, acidosis, chronic heart failure (CHF) [Class III-IV functional class according to NYHA (classification of the New York Heart Association)], pulmonary edema, cerebral edema, hypercoagulation, hypervolemia, thrombophlebitis, metabolic alkalosis, chronic renal failure (CRF) with oligo- and anuria, concomitant therapy with glucocorticosteroids.
With caution. Arterial hypertension; cardiovascular diseases (including chronic heart failure NYHA functional class I-II), concomitant administration of cardiac glycosides, concomitant administration with blood products due to risk of coagulation; hepatic insufficiency; pre-eclampsia; peripheral edema of various genesis; Hyperaldosteronism and other pathologies associated with hypernatriemia or hyperkalemia (mild to moderate renal failure, adrenal insufficiency, acute dehydration, extensive tissue decay); diseases and conditions predisposing to increased vitamin D concentration (including sarcoidosis). Use in pregnancy and during breast-feeding. Research of possibility of using Ringer’s solution during pregnancy and breast-feeding has not been carried out. In this regard, the drug should be used in pregnant women only after the assessment of the benefit/risk ratio and during the use in breast feeding women it is necessary to refrain from breast feeding.
Dosage and administration method
- Intravenously (IV) in a drop-flow at a rate of 60 to 80 drops/min, in patients with severe state – 70-90 drops/min or by jetting. The volume of fluid administered depends on the type of dehydration, the degree of dehydration and body weight of the patient, the cause of shock.
- The daily dose for adults is 5-20 ml/kg; if necessary, it can be increased to 30-50 ml/kg.
- The daily dose for children is 5 to 10 ml/kg and the infusion rate is from 30 to 60 drops/min; in case of shock dehydration, 20 to 30 ml/kg is injected first. The course of treatment is 3-5 days.
- With therapeutic plasmapheresis is administered in a volume two times the volume of plasma removed (1.2-2.4 liters), in case of severe hypovolemia – in combination with colloidal solutions.
- In mild and moderate degrees of severity of acute intestinal infections the drug can be used only when oral rehydration is impossible. During prolonged administration of large doses of the drug it is necessary to monitor the electrolyte composition of blood plasma and urine.
- The maximum volume of administered solution is 3 l/day.